Understanding Autism: A Biomedical Approach to Training and Treatment

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. As parents of autistic children, you may often find yourself navigating a maze of information, therapies, and treatment options. One approach that has gained traction in recent years is the biomedical model, which posits that by modifying certain environmental factors, we can help improve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for autistic individuals.
The Genetic Component of Autism
Autism is believed to have a genetic basis, with studies indicating that certain genetic factors may predispose individuals to develop the condition. However, it’s crucial to understand that not all genetic components are set in stone. Some genetic expressions can be influenced by environmental factors, meaning that changes in the environment can potentially modify how these genes function.
One such gene of interest is the **MTHFR gene**. To simplify, the MTHFR gene is responsible for producing an enzyme that helps process amino acids—the building blocks of proteins—and is essential for the body's ability to use folate (a type of B vitamin). This gene plays a significant role in the methylation process, which is involved in regulating many bodily functions, including DNA repair and detoxification.
When the MTHFR gene is not functioning optimally—often due to mutations—this can lead to a variety of health issues, including problems with metabolism and mental health. In the context of autism, some researchers believe that supporting the body's methylation process through dietary changes and supplements can help address certain symptoms associated with the disorder.
The Role of Environment in Modifying Autism
The biomedical approach emphasizes the idea that while some genetic factors may be permanent, many are modifiable through environmental changes. This could include dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and the use of specific supplements aimed at enhancing overall health and well-being.
For instance, research has shown that certain dietary interventions, such as gluten-free or casein-free diets, can lead to improvements in behavior and communication skills in some children with autism. Furthermore, ensuring adequate intake of vitamins and minerals, particularly those involved in the methylation process, can support brain health and function.
A study published in *The Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders* found that children with autism who were supplemented with methylcobalamin (a form of vitamin B12) showed improvements in communication and social skills. This illustrates the potential impact of targeted nutritional support in managing autism symptoms.
The Mind-Body Connection
Another aspect of the biomedical approach is addressing the mind-body connection. Many doctors and scientists argue that by focusing on mental health and emotional well-being, we can facilitate better outcomes for autistic individuals. Stress, anxiety, and other emotional factors can exacerbate the challenges faced by children with autism. Therefore, therapies that promote mental wellness—such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques—can play a vital role in treatment.
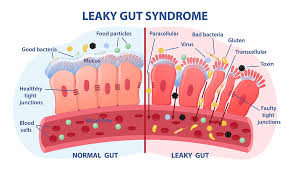
Furthermore, some researchers are investigating how gut health may influence autism symptoms. The gut-brain connection is increasingly recognized in modern medicine, and studies suggest that a healthy gut microbiome may positively impact behavior and cognitive function. This underscores the importance of a holistic approach that considers both physical and mental health.
Conclusion
While autism has genetic components that may be permanent, the biomedical approach offers hope for parents seeking to improve their child's condition through modifications in environment and lifestyle. By understanding the role of genes like MTHFR and the impact of nutrition and mental health, we can empower ourselves to make informed decisions about treatment options.
As research continues to evolve, staying informed and connected with healthcare professionals who specialize in autism is essential. Remember, every child is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Nevertheless, with the right support and interventions, the journey toward improved well-being for autistic individuals can be a positive and transformative experience.
If you’re interested in exploring more about the biomedical approach to autism, consider connecting with professionals or support groups that focus on this area. Together, we can create a brighter future for our children.